Why Fourier Transform Near-Infrared (FT-NIR) Spectrometers Outperform Conventional NIR Analyzers in Multi-Industry Applications
May 21, 2025
Unlocking Broader Analytical Capabilities with Advanced Spectral Precision
Near-infrared (NIR) spectroscopy has long been a cornerstone of rapid, non-destructive quality analysis. However, not all NIR technologies are created equal. Fourier Transform Near-Infrared (FT-NIR) spectrometers, with their superior design and performance, are increasingly displacing conventional dispersive or filter-based NIR systems in industries ranging from pharmaceuticals to agriculture. Here’s why FT-NIR technology offers unmatched versatility and precision, making it indispensable for modern quality control and process optimization.
1.The Science Behind FT-NIR: Precision Meets Speed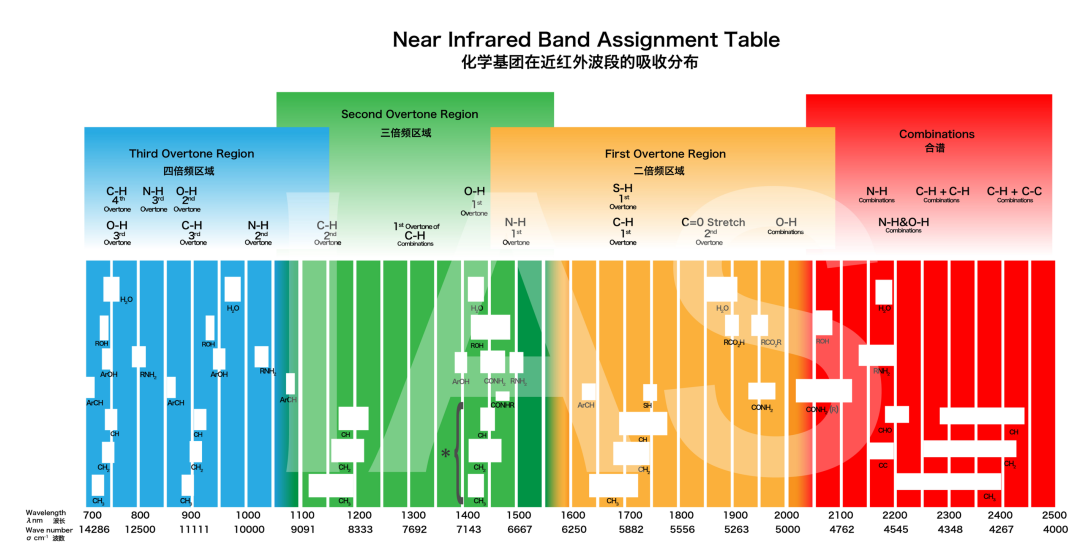
How FT-NIR Works
Unlike conventional NIR analyzers that rely on diffraction gratings or filters to isolate wavelengths, FT-NIR spectrometers use an interferometer and a Michelson interferometry principle. This setup splits light into two beams, recombines them after a path difference, and generates an interferogram. A Fourier Transform algorithm then converts this raw data into a high-resolution spectrum.
Key Advantages Over Conventional NIR:
Higher Spectral Resolution: FT-NIR achieves resolutions up to 5 cm<sup>-1</sup>, capturing subtle spectral details critical for complex mixtures (e.g., pharmaceuticals, polymers).
Wider Wavelength Range: Covers 4,000–12,000 cm<sup>-1</sup>(1,000–2,500 nm), enabling detection of diverse chemical bonds (C-H, O-H, N-H, S-H).
Faster Scan Speeds: Full-spectrum acquisition in 1–2 seconds, ideal for real-time monitoring in fast-paced production lines.
2. Expanding Applications: Where FT-NIR Shines
a.Pharmaceuticals & Fine Chemicals
Conventional NIR systems struggle with trace impurity detection in active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). FT-NIR’s high resolution identifies low-concentration components (e.g., residual solvents, polymorphs) with ±0.1% accuracy, ensuring compliance with USP/ICH guidelines.
b.Food & Agriculture
Grain and Oilseed Analysis: FT-NIR quantifies protein (8–25%), moisture (8–22%), and oil content (15–30%) while simultaneously detecting mycotoxins (e.g., aflatoxin B1 at 50 ppb).
Dairy & Beverages: Measures fat, lactose, and moisture in milk powders with R² >0.99against reference methods.
c.Polymer & Petrochemicals
FT-NIR distinguishes between polymer blends (e.g., PE/PP ratios) and monitors curing reactions in real time, a task beyond the reach of filter-based NIR.
|
Challenge |
Conventional NIR |
FT-NIR Solution |
|
Low-Resolution Data |
Misses fine spectral features |
Detects trace components (e.g., 0.1% impurities) |
|
Slow Scanning |
10–30 seconds per sample |
1-second scans enable inline process control |
|
Limited Wavelength Range |
Narrow range (e.g., 1,200–2,400 nm) |
Full-spectrum coverage for diverse applications |
|
Calibration Drift |
Frequent recalibration required |
Stable interferometers reduce drift |
4.IAS ANALYSIS FT-NIR Innovations: Bridging Technology and Industry Needs
IAS ANALYSIS’s next-generation FT-NIR analyzers, integrate cutting-edge innovations:
Ruggedized Interferometers: Maintain precision in high-vibration environments (e.g., feed mills, chemical plants).
AI-Driven Calibration: Self-optimizing models adapt to matrix variations, reducing calibration effort by 50%.
Industry 4.0 Readiness:
IAS systems seamlessly connect to PLCs, MES, and cloud platforms, transforming spectral data into predictive maintenance alerts or automated process adjustments.
